Publication 3:A comprehensive Prosthodontic Management of subtotal Maxillectomy.
Publication 3: A comprehensive Prosthodontic Management of subtotal Maxillectomy.
ABSTRACT
Patient: A 21-year-old female patient was diagnosed with intraosseous mucoepidermoid carcinoma on the left side of maxilla, which was planned for subtotal maxillectomy involving the left maxillary sinus.
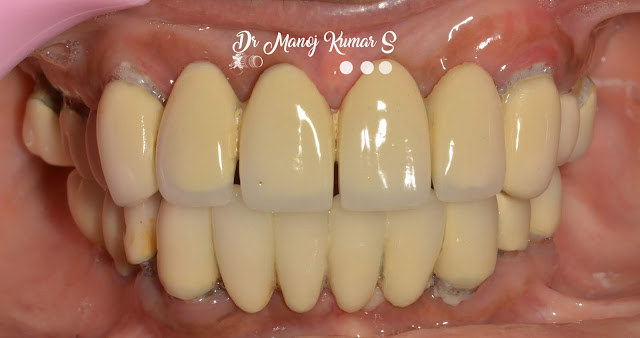
Discussion: Prosthodontic rehabilitation of patients with maxillectomy is a challenge as it involves restoring speech, deglutition, mastication and respiration. This clinical report describes a comprehensive prosthodontic management of a young girl treated for a subtotal maxillectomy due to intraosseous mucoepidermoid carcinoma. The prosthodontic management that was carried out right from the surgical obturator to a definitive prosthesis with a two-piece closed hollow bulb, magnet-retained obturator shows the ease and simplicity in the management of a case with subtotal maxillectomy.
Conclusion: Subtotal maxillectomy defects represent a complex challenge for the maxillofacial prosthodontist. The comprehensive technique described in this clinical report can be employed in any similar case.
Keywords: Magnet, Maxilla, Osteotomy, Palatal, Obturator, Prosthesis design, Speech, Intelligibility.
How to cite this article: Sundar MK, Kumar GPS, Lakhanpal S. A Comprehensive Prosthodontic Management of Subtotal Maxillectomy. Int J Prosthodont Restor Dent 2014;4(4):120-126.
For complete article look up to the link:
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f081/b5b532d24eec71a0c93341d3da73e3bb665c.pdf
ABSTRACT
Patient: A 21-year-old female patient was diagnosed with intraosseous mucoepidermoid carcinoma on the left side of maxilla, which was planned for subtotal maxillectomy involving the left maxillary sinus.
Discussion: Prosthodontic rehabilitation of patients with maxillectomy is a challenge as it involves restoring speech, deglutition, mastication and respiration. This clinical report describes a comprehensive prosthodontic management of a young girl treated for a subtotal maxillectomy due to intraosseous mucoepidermoid carcinoma. The prosthodontic management that was carried out right from the surgical obturator to a definitive prosthesis with a two-piece closed hollow bulb, magnet-retained obturator shows the ease and simplicity in the management of a case with subtotal maxillectomy.
Conclusion: Subtotal maxillectomy defects represent a complex challenge for the maxillofacial prosthodontist. The comprehensive technique described in this clinical report can be employed in any similar case.
Keywords: Magnet, Maxilla, Osteotomy, Palatal, Obturator, Prosthesis design, Speech, Intelligibility.
How to cite this article: Sundar MK, Kumar GPS, Lakhanpal S. A Comprehensive Prosthodontic Management of Subtotal Maxillectomy. Int J Prosthodont Restor Dent 2014;4(4):120-126.
For complete article look up to the link:
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f081/b5b532d24eec71a0c93341d3da73e3bb665c.pdf

Comments